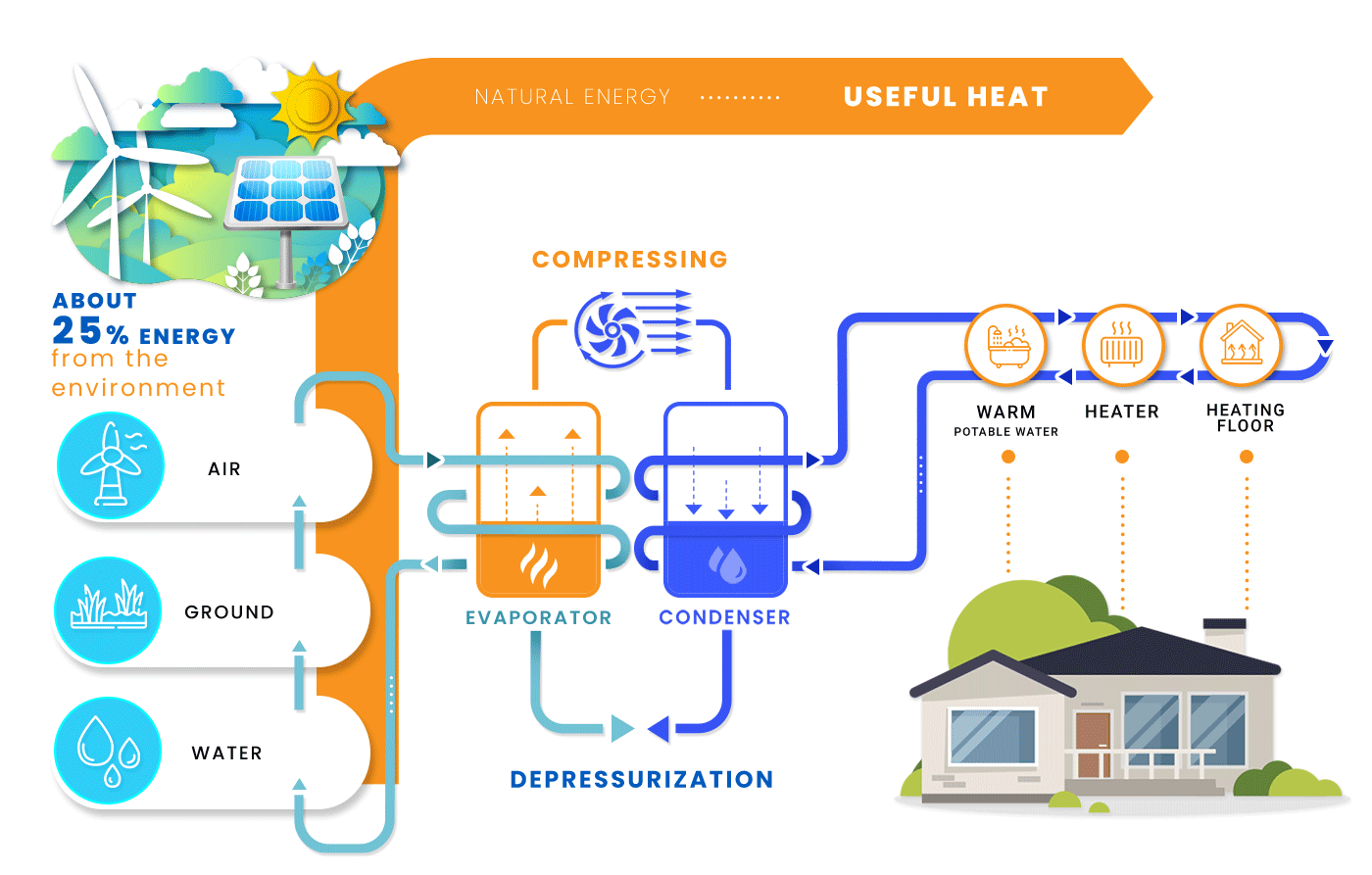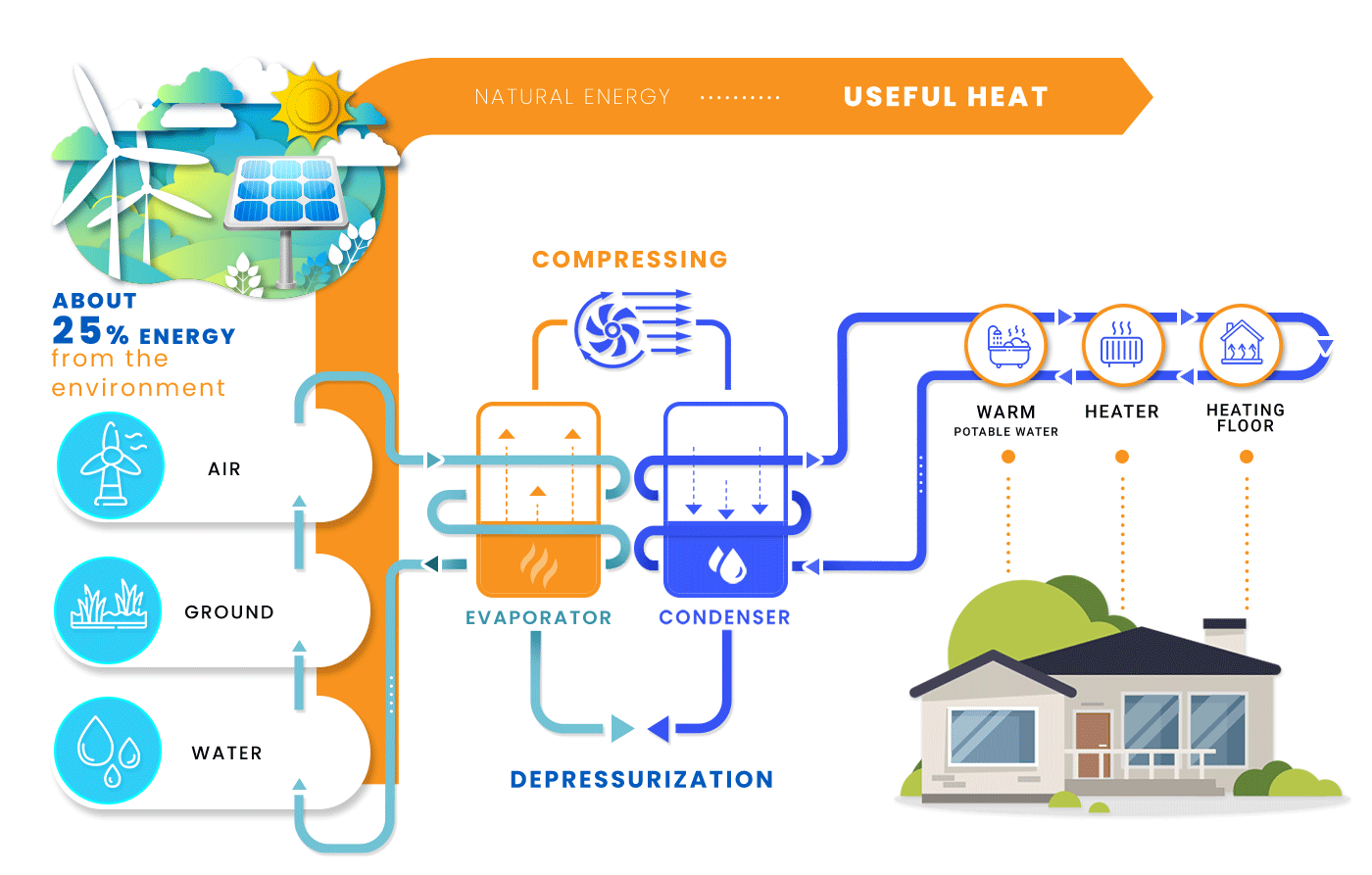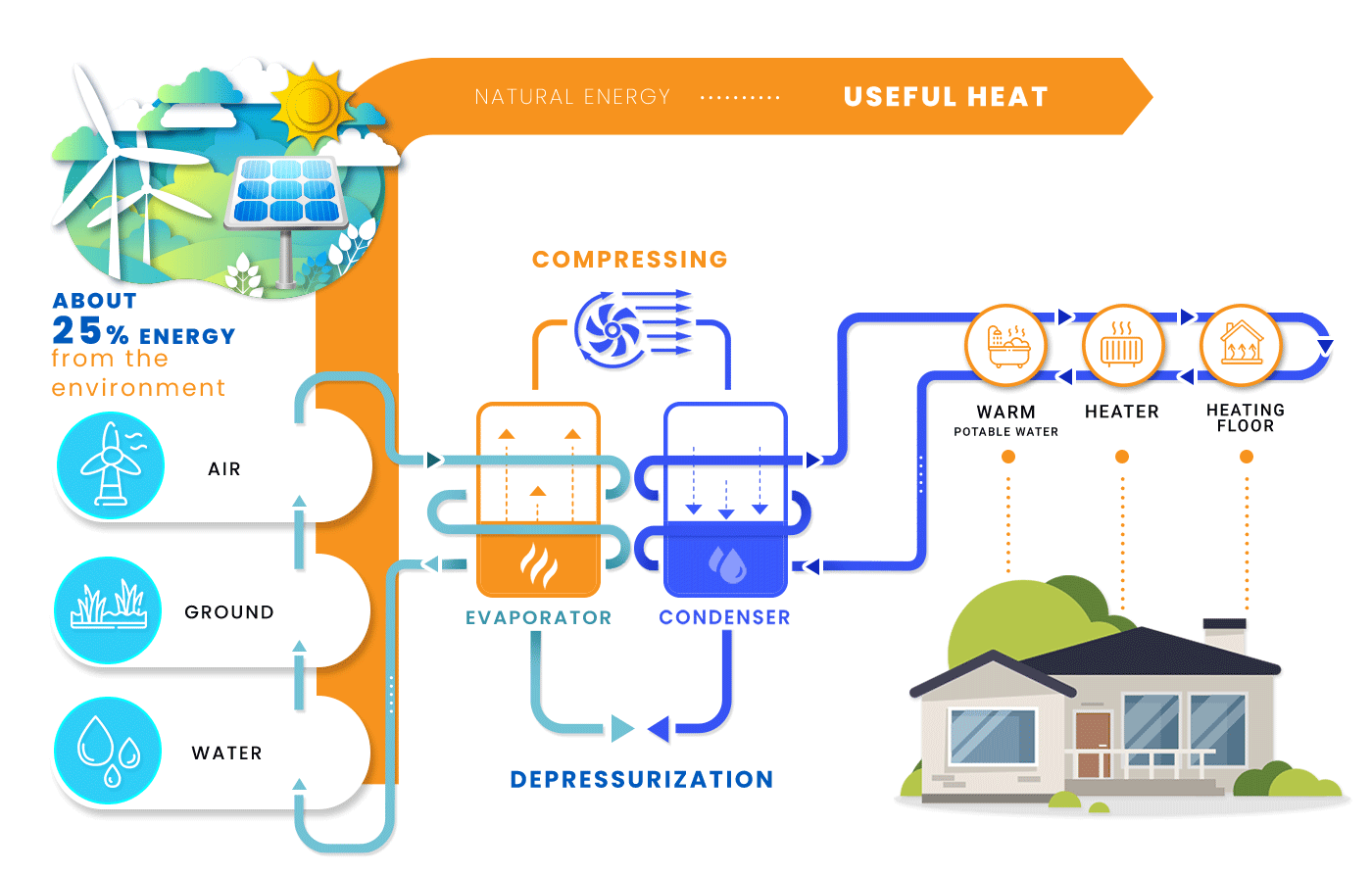
The operation of the heat pump is based on a simple mechanism. Heat pumps take heat energy from a reliable source, the temperature of which is lower than in the heated room, and convert this heat so that it has a higher temperature than at the beginning.
This mode of operation is often compared to the operation of a refrigerator, which takes heat from the products it contains and gives it away to the environment. The heat pump works in the same way. A suitable heat pump installation (e.g. a system of water-filled glycol pipes) extracts heat from the soil, air, or groundwater then condenses this heat using a compressor and gives it to its surroundings.